The rate at which new oceanic lithosphere is added to each tectonic plate on either side of a mid ocean ridge is the spreading half rate and is equal to half of the spreading rate.
The seafloor spreading process at ridges produces what kind of faults quizlet.
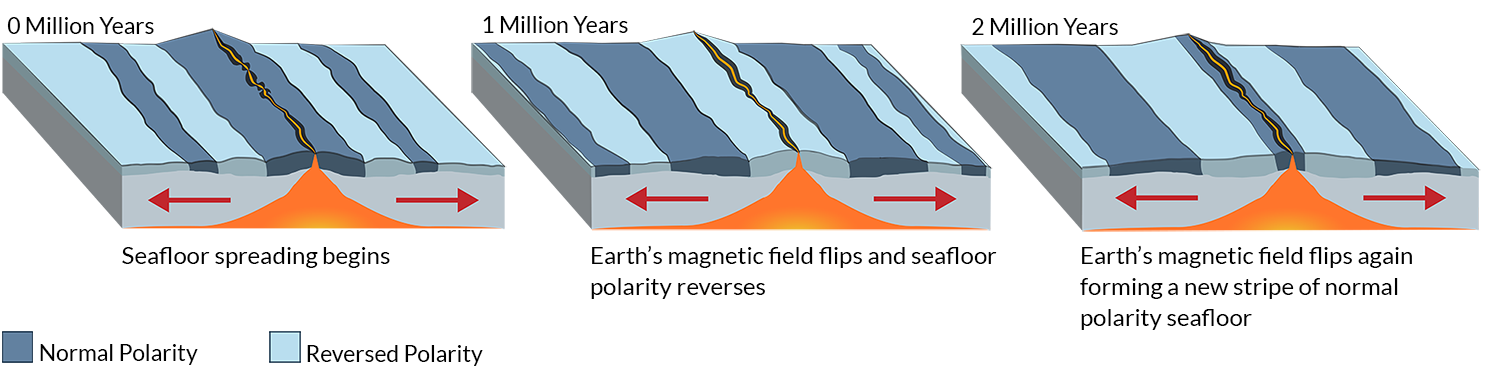
Magma is pushed up through cracks in the crust along the mid ocean ridge.
The seafloor spreading process at ridges produces what kind of faults.
As the magma is thrust up and hardens it forms new crust and the ocean floor on both sides of the mid ocean ridge move outward.
The formation of the new crust is due to the rising of the molten material magma from the mantle by convection current.
The process of sea floor spreading.
Volcanoes mountain ranges deep ocean trenches.
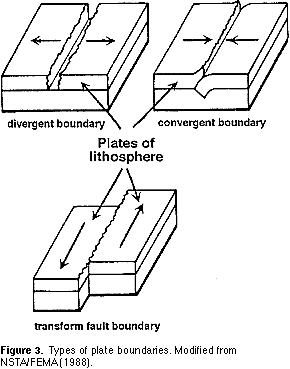
The place where 2 plates come together or converge.
The indian ocean has no oceanic ridge.
This idea played a pivotal role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics which revolutionized geologic thought during the last quarter of the 20th century.
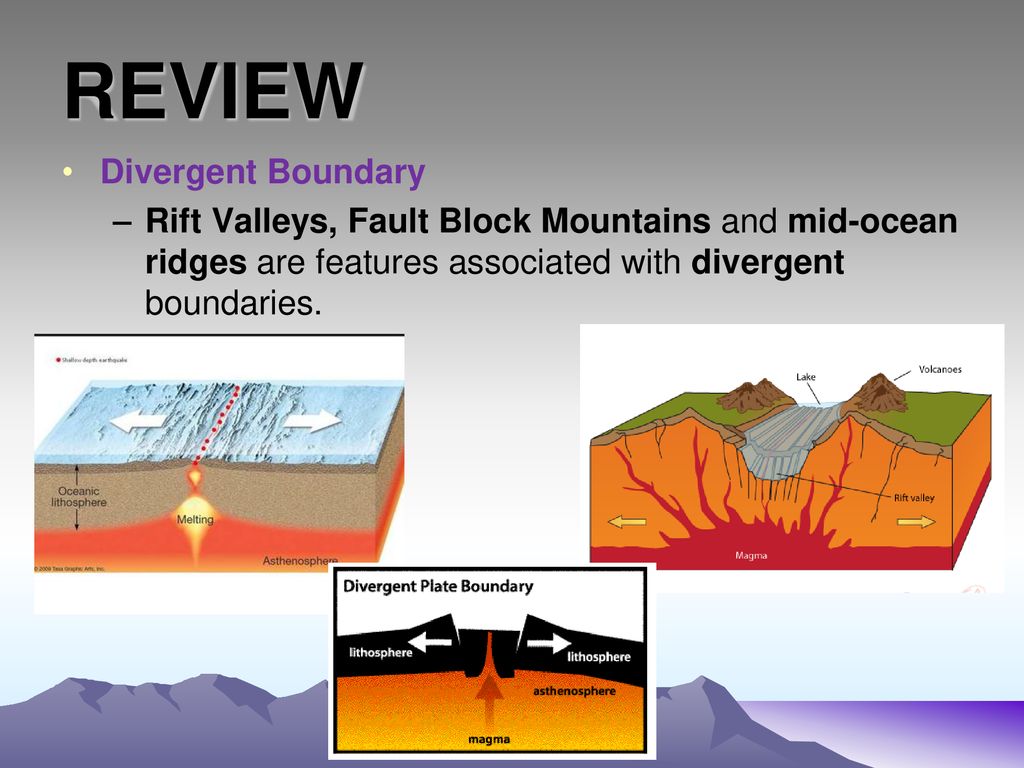
The mid ocean ridge is the region where new oceanic crust is created.
Along the mid ocean ridges where sea floor spreading occurs.
Sea floor spreading occurs when the sea floor spreads apart along divergent boundaries and forms the mid ocean ridge.
Basalt the once molten rock that makes up most new oceanic crust is a fairly magnetic substance and scientists began using magnetometers to measure the magnetism of the ocean floor in the 1950s what they discovered was that the magnetism of the ocean floor around.
Seafloor spreading is a process that occurs at mid ocean ridges where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.
The seafloor spreading process at ridges produces what kind of faults.
Seafloor spreading takes place at midocean ridges and produces basalt the rock that makes up the oceanic crust.
Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics.
The mid atlantic ridge and east pacific rise are examples of midocean ridges.
The process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor.
The lithosphere cools as it moves away from the ridge axis by sea floor spreading and cooler rocks are lower density so the sea floor gets deeper as the lithosphere gets more dense.
The magnetism of mid ocean ridges helped scientists first identify the process of seafloor spreading in the early 20th century.
Spreading rates determine if the ridge is fast intermediate or slow.
They are the shallowest major features of the seafloor.
Midocean ridges reach a typical summit elevation of 2 700 meters below sealevel.
Seafloor spreading theory that oceanic crust forms along submarine mountain zones known collectively as the mid ocean ridge system and spreads out laterally away from them.
Normal faults the atlantic and pacific basins have oceanic ridges.